Candid API - Apply Titles and Footnotes stored in Candid to your TFLs
big thank you to Alisa Solomatina, our Summer 2024 Intern, for writing this article and for writing our package of example Candid API calls using the R programming lanaguage!
At the heart of Candid's data accessibility lies its robust API (Application Programming Interface) – a tool which allows you to directly interact with Candid database programmatically. It provides a way to retrieve, update, and manage data without the need for manual intervention, opening up opportunities for task automation and streamlining processes such as creation of TFLs.
If not sure where to start, the Candid API documentation page is a great way to begin your journey with the API (your Candid user account must have API access activated in order to view and use the API help page). The API Help provides detailed descriptions of available API calls, endpoints, parameters, and example values/responses. It also features an interactive interface that lets you try out and experiment with API calls directly within Candid – so you can interact with the live data and see the results in real-time without the need for extra programming or any other software.
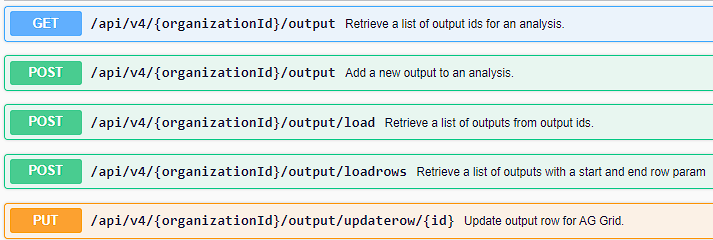
There are many ways how the API can be used to interact with the Candid
database.
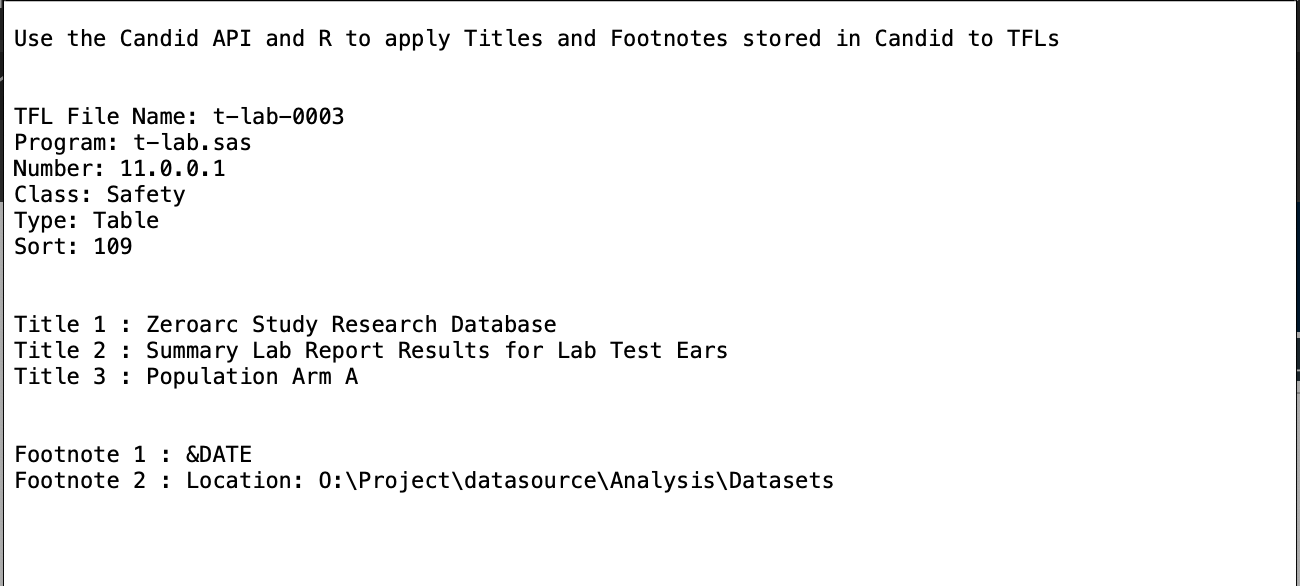
Here is an example where R and the API are working together to retrieve TFL
metadata, titles and footnotes and then merge them together, simulating creation of
a TFL:
For performance and security reasons, Candid API uses same 2-step pattern for
retrieving data. First, a GET request is used to retrieve the IDs of an object type (TFLs, Issues,
Test Results etc). And after that, these IDs are sent back to the server in the body of a POST request
to get back the details for each of the IDs sent.
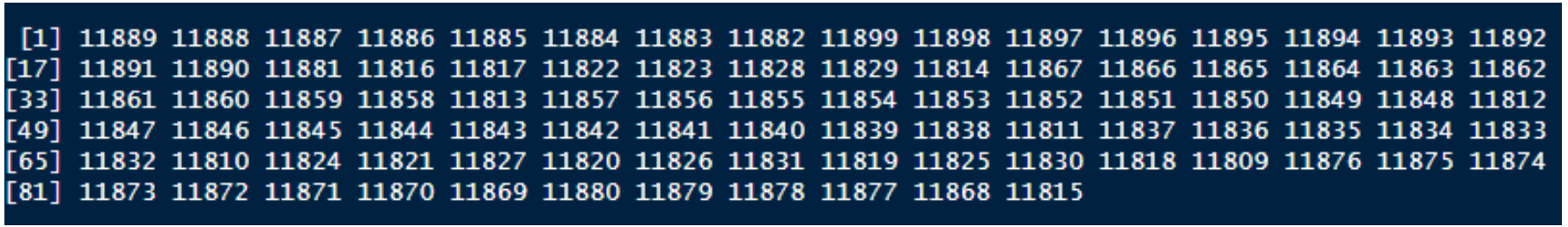
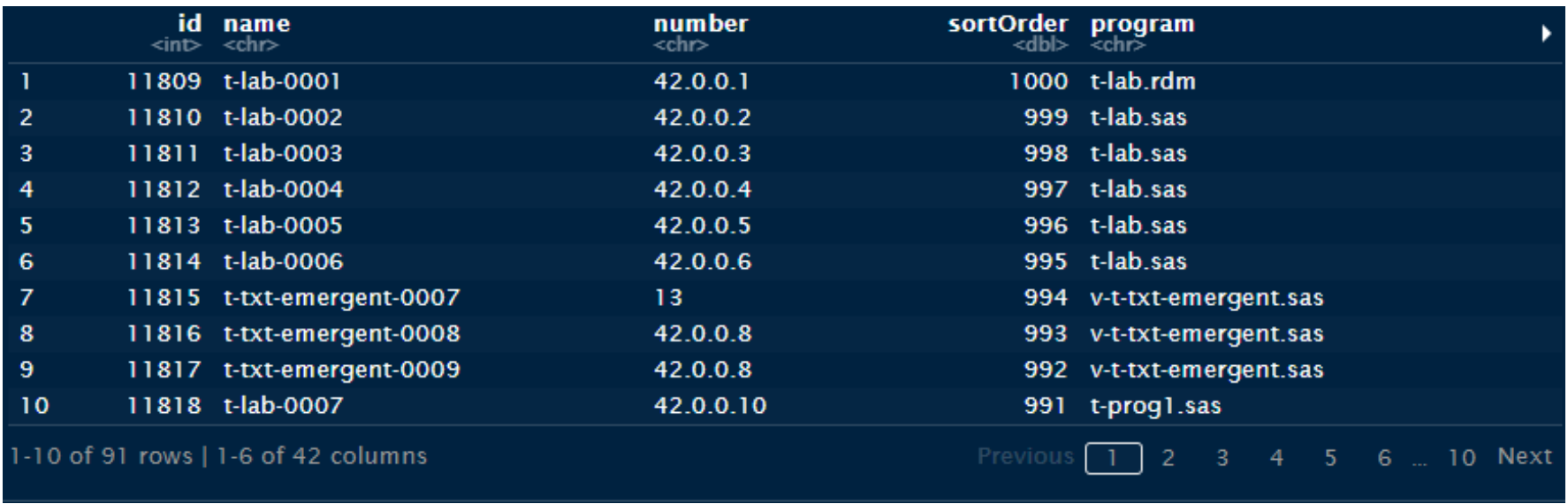
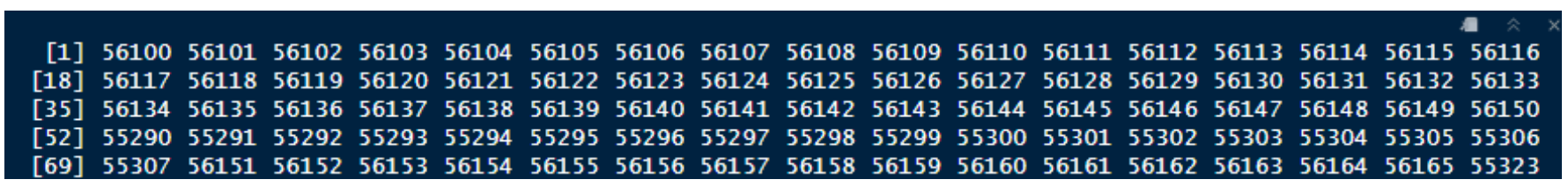
First step is to retrieve TFL IDs through a GET request – output would usually be an array of integers (IDs):

Learn More
Contact us to see code examples in R, request a free Candid trial or for more information about Candid and its features, please visit zeroarc.com or schedule a free demo.